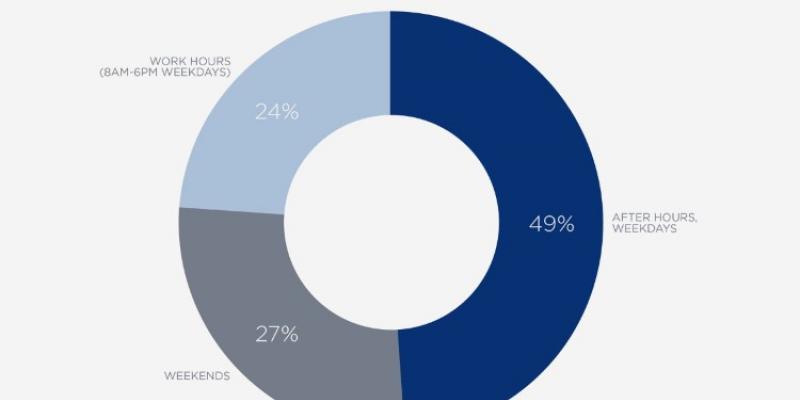
Most Ransomware Attacks Take Place Outside Working Hours
According to a report published by US cyber-security FireEye, 76% of all ransomware infections in the enterprise sector occur outside working hours, with 49% taking place during nighttime over the weekdays, and 27% taking place over the weekend.
The numbers, FireEye said, were compiled from dozens of ransomware incident response investigations from 2017 to 2019.
The reason why attackers are choosing to trigger the ransomware encryption process during the night or weekend is because most companies don't have IT staff working those shifts, and if they do, they are most likely short-handed.
If a ransomware attack does trigger a security alert within the company, then there would be nobody to react right away and shut down a network, or the short-handed staff would have a hard time figuring what's actually happening before the ransomware encryption process ends and the company's network is down & ransomed.
FireEye says that ransomware gangs breach a company's network, spend their time moving laterally to as many workstations as possible, and then manually install ransomware on all systems and trigger the infection.
The time from initial compromise to the actual ransomware attack -- known as a "dwell time" -- is, on average, three days, according to FireEye.
FireEye said that since 2017, human-operated ransomware attacks have gone up 860%, and incidents now impact all sectors and all geographical locations, and not just North American companies.
In the cases FireEye investigated the most common infection vectors were:
- Brute-force attacks against workstations with RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) ports open on the internet
- Spear-phishing against a company's employees and using one infected host to spread to others
- Drive-by downloads (employees visiting a compromised website and downloading malware-infected files).
FireEye is now urging companies to invest in deploying detection rules for spotting attackers during their pre-infection "dwell time."
"If network defenders can detect and remediate the initial compromise quickly, it is possible to avoid the significant damage and cost of a ransomware infection," FireEye said.











